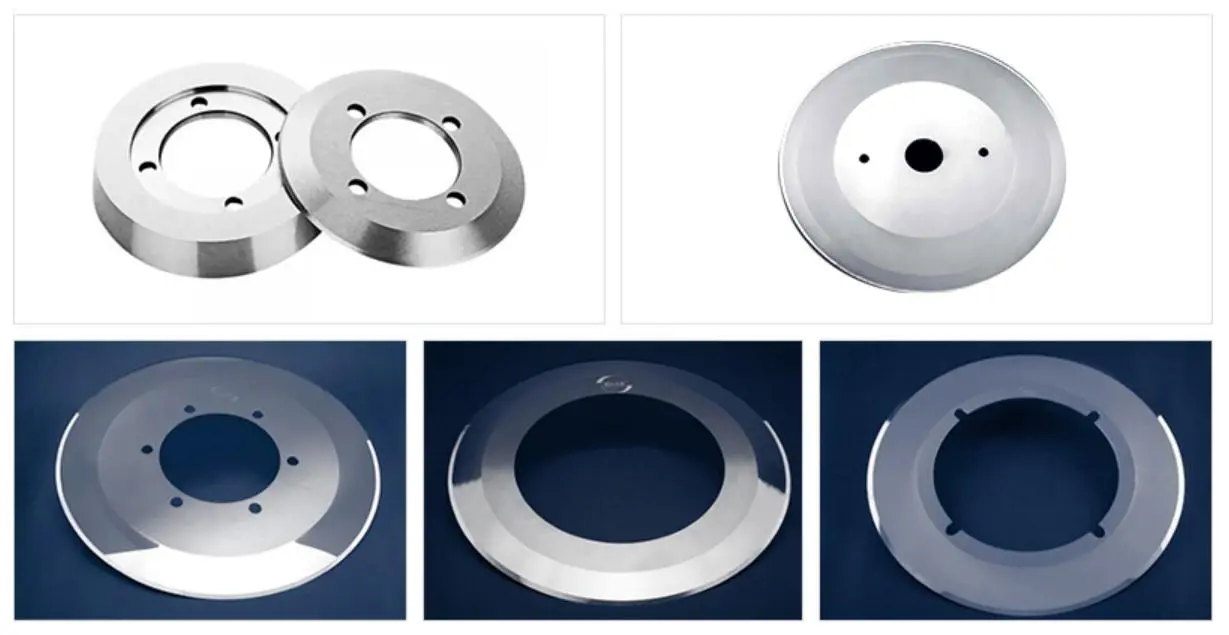
The Introduction of Cemented Carbide from all over the world
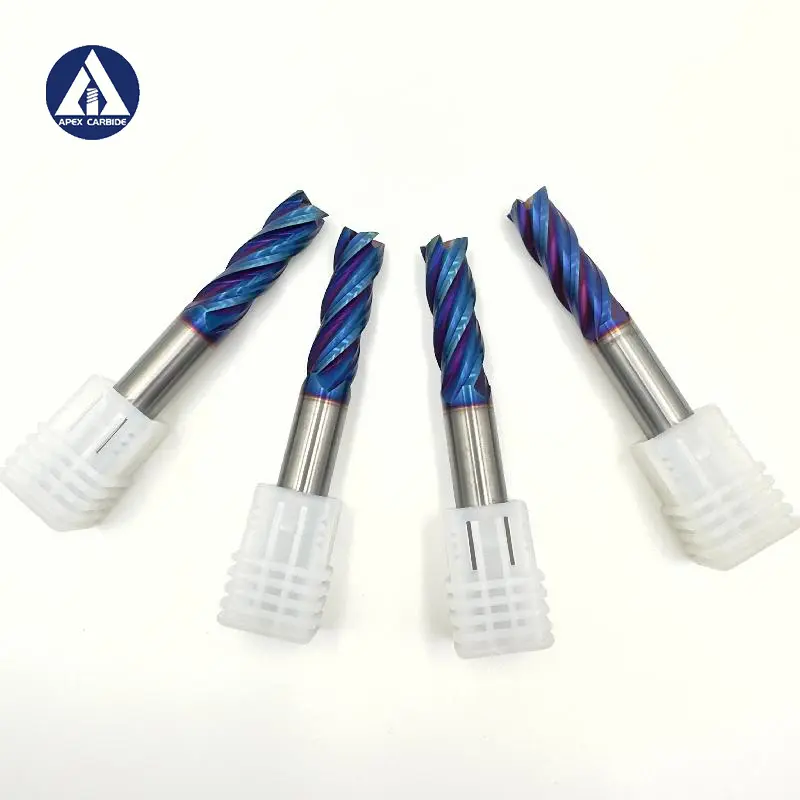
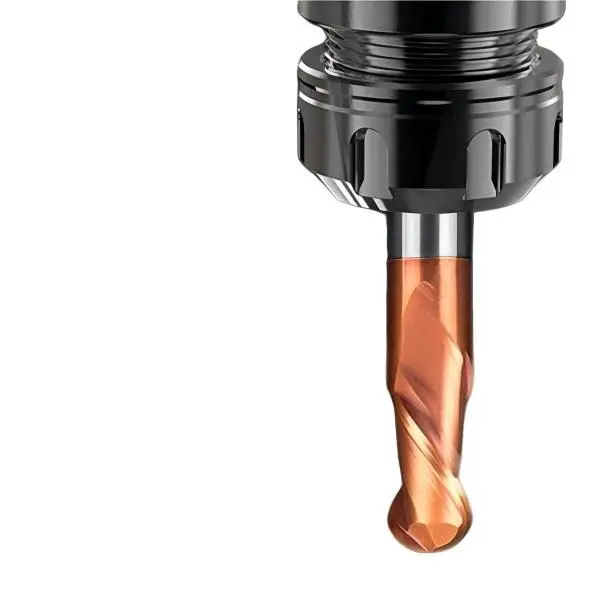
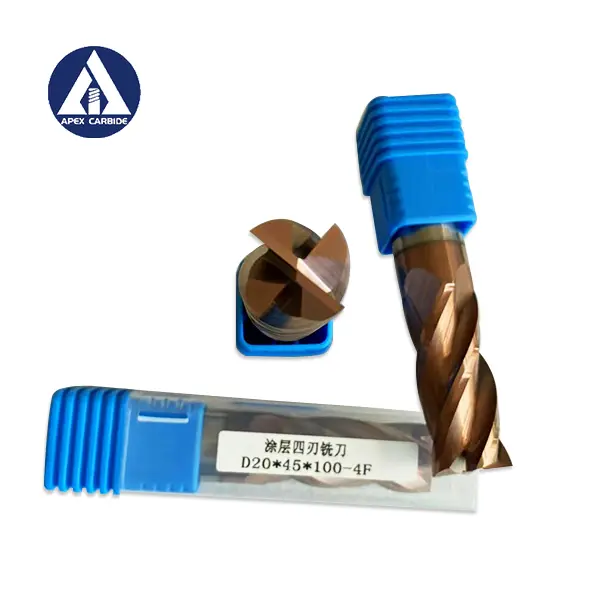
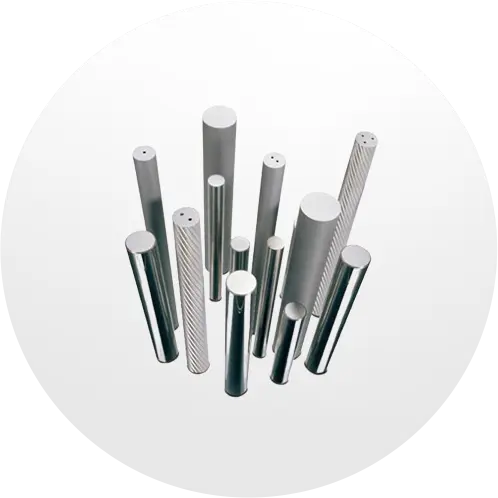
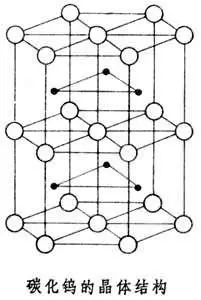
Cemented Carbide is a powder metallurgy product with high strength and high wear resistance made of refractory metal carbide as the main component and metal as binder. Refractory metal compounds refer to transition metal carbides of Groups IV, V, and VI of the periodic table of elements, mainly WC, TiC and TaC. The bonding metals are generally iron group metals, among which cobalt is commonly used. Cemented carbide combines the high hardness and high wear resistance of the carbide phase with sufficient mechanical properties and thermal shock resistance of the metal binder phase, making it widely used in many fields.
In Europe, cemented carbide is generally referred to as "hard metal". Cemented carbide was successfully developed by Germany in the early 1920s, and the main inventor was K. Schroter. He successfully developed tungsten-cobalt cemented carbide by powder metallurgy in 1923. In 1927, German Fried Krupp Company first carried out industrial production of cemented carbide and put it on the market under the trademark of "Widia". In 1953, the United States first used indexable inserts, which caused a major change in the field of cemented Carbide Tools. In 1959, German Metal Company successfully developed TiC-coated cemented carbide, which was deposited on the surface of cemented carbide by vapor deposition. Apply one or more thin layers of wear-resistant refractory hard compound. In 1946, the Krupp company of the Federal Republic of Germany successfully carried out the production of TiC-coated cemented carbide. After coating the indexable blade, the service life can be increased several times, and the cutting speed can be increased by 25% to 30%. Another major development in the alloy industry.
There are more than 50 countries in the world producing cemented carbide, with a total output of 27,000-28,000 tons. The main producers are the United States, Russia, Sweden, China, Germany, Japan, the United Kingdom, France, etc. The world cemented carbide market is basically in a saturated state. The market competition is fierce. China's cemented carbide industry began to form in the late 1950s. In the 1960s and 1970s, China's cemented carbide industry developed rapidly. In the early 1990s, the total production capacity of China's cemented carbide reached 6000t, and the total output of cemented carbide reached 5000t, second only to China's cemented carbide industry. In Russia and the United States, ranking third in the world.
The use of cemented carbide can be divided into 4 categories: P-type alloys are mainly used for steel cutting; K-type alloys are mainly used for cast iron and non-ferrous metal processing; M-type alloys are general-purpose alloys that can be used for steel, cast iron and non-ferrous metals at the same time cutting; G-type alloys can be used as mining and wear-resistant tools. The number of the above-mentioned alloy codes increases from top to bottom, the strength of the alloys increases sequentially, the hardness decreases sequentially, the impact resistance increases sequentially, and the wear resistance decreases sequentially. Alloys with smaller codes should be used for finishing tools, and alloys with larger codes should be used for roughing tools.